Nuts and bolts are the backbone of fastening technology, widely used in industries, construction, and even household applications. Whether you are assembling furniture, constructing a bridge, or working on machinery, nuts and bolts play a critical role in providing strong and secure connections. In this guide, we will explore the types of nuts and bolts, understand the difference between nut and bolt, and discuss their applications.
What is a Nut and a Bolt?
Before diving into the different types, let’s clarify what nuts and bolts are and how they function.
A bolt is a threaded fastener with a head on one end and a shaft on the other. The shaft is designed to pass through pre-drilled holes and is secured in place using a nut. A nut is a small metal block with an internal thread that matches the bolt’s thread, allowing them to be fastened together.
Bolts provide the tensile strength, while nuts hold the assembly together, creating a reliable and secure joint. The primary function of these components is to ensure that parts stay firmly attached under pressure, vibrations, and movement.
Difference Between Nut and Bolt
While nuts and bolts are often used together, they serve distinct purposes. Here are the key differences between nut and bolt:
| Feature | Nut | Bolt |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A nut is a small metal fastener with an internal thread. | A bolt is a metal rod with an external thread and a head. |
| Function | Secures a bolt in place by threading onto it. | Passes through materials and holds them together when tightened with a nut. |
| Shape | Typically hexagonal but can come in different shapes. | Comes in various head styles, including hex, round, and square. |
| Usage | Used with bolts or screws to secure components. | Used with nuts or tapped holes to fasten materials. |
Types of Nuts and Bolts
There are various types of nuts and bolts, each designed for specific applications. Understanding these types helps in choosing the right fastening solution for your project.
Types of Bolts
-
Hex Bolts
These are the most commonly used bolts, featuring a six-sided head. They are widely used in construction, automotive, and machinery applications. -
Carriage Bolts
Carriage bolts have a round head with a square section under it. This prevents the bolt from spinning when tightened with a nut. -
Flange Bolts
These bolts come with a built-in washer-like flange under the head, which helps distribute the load and reduces the need for an extra washer. -
Lag Bolts
Also known as lag screws, these bolts have a hex head and are designed for heavy-duty applications, especially in wood structures. -
Anchor Bolts
Used for securing structures to concrete, these bolts come in different shapes such as L-shaped, J-shaped, and U-shaped. -
U-Bolts
These bolts have a U-shape and are commonly used for securing pipes or round objects. -
Eye Bolts
Featuring a loop (eye) at one end, these bolts are used for lifting or anchoring applications. - Domed Bolts
These decorative bolt heads are difficult to wrench externally, which adds a level of security.
- Bent Bolts
The example shown here is an eye bolt for lifting, but bolts are available in other shapes for speciality applications
- Square Bolts
Enables an easy grip for wrenches for tightening nuts
- Pentagon Bolts
Designed to resist tampering by not accommodating torx and hex tools
- Flat Bolts
Flat head bolts are countersunk, which enables them to save space on applications.
- Anchor Bolts
Used in the construction industry to secure a structural component to a concrete slab or poured foundation.
- Blind Bolts
For structural applications where access is restricted to one side, enabling the lock to still be completed.
-
Double end Bolts
A bolt with threads on both ends, also called stud bolts. Used to fasten two flanges or pipes more effectively.
-
Eye Bolts
Used for lifting applications. Some are designed for heavy loads while others are for non-load bearing uses.
-
Penta-head Bolts
Highly specialized bolt with five-sided head. Typically used for security on manhole covers and ground lids.
-
Shoulder Bolts
Performs as a shaft or axle that can hold a rotating part, such as a bearing. Also called a shoulder screw and stripping bolt.
-
T Head Bolts
Also known as a T-slot. Inserts into a recess and with the applied nut, the bolt is secured against turning. Common in construction and automotive.
-
J-Bolt Bolts
Also referred to as a hook bolt and typically used in structural applications, such as roofing and securing walls to concrete foundations.
-
Elevator Bolts
Named after its original use in grain elevator systems. Today it’s used on assembly lines, furniture and various consumer products. Large circular head and low profile provides generous clearance
-
Flange Bolts
The flange acts as a washer to distribute the load. Commonly used to connect plumbing pipes, a vehicle’s transmission and engine and other mechanical applications.
-
Hanger Bolts
Connects two surfaces while hiding the bolt. Often used to suspend electrical conduits, fixtures and sheet metal.
Types of Nuts
-
Hex Nuts
These are standard six-sided nuts used with hex bolts for general fastening applications. -
Lock Nuts
Designed to resist loosening under vibration or pressure, lock nuts come in various types, including nylon insert nuts and metal lock nuts. -
Wing Nuts
Wing nuts have protruding ‘wings’ that allow hand-tightening without tools, making them easy to adjust and remove. -
Flange Nuts
Similar to flange bolts, these nuts have a built-in washer-like surface to distribute the load and prevent damage to materials. -
T-Nuts
Used in wood and furniture applications, T-nuts have prongs that dig into the material to provide a secure hold. -
Cap Nuts (Acorn Nuts)
These nuts have a domed top to cover the exposed end of a bolt, providing both safety and a neat appearance. -
Square Nuts
Featuring a four-sided shape, these nuts offer a larger surface area for better grip and load distribution. - Dome Nuts
Protects bolt threads underneath while presenting a clean appearance. Also can prevent skin and clothes from snagging on sharp edges.
- Acorn Nuts
A type of cap nut with the same capabilities. Named after its head, which is shaped like an acorn. Cap nuts are used across all industries and also resist vibration.
- Wing Nuts
The side wings enable quick, easy tightening and removal by hand. For this reason, it should not be used if vibration is present.
-
Jam Nuts
Low-profile nuts that, when jammed into place against a standard nut, prevents loosening. Also used when a standard nut won’t fit.
-
Flange Nuts
The flange serves the purpose of a washer, evenly distributing the load. Typically used in the automotive sector on exhausts.
-
Coupling Nuts
While not typically a bolt nut, these are used for connecting threaded rods or pipes together.
-
Nyloc Nuts
Insert creates friction, resulting in a gripping action and reducing chance of loosening due to vibration. Commonly used in white goods, computers and vehicles
-
Tee Nuts
For fastening soft materials such as wood or plastic. The flange on one side has hooks, which latch onto the material being fastened to strengthen the joint and leave a flush surface.
-
Slotted Nuts
Secured using a cotter pin or wire to prevent rotation. Typically used in applications where vibration is a constant threat.
-
Castle Nuts
The turret geometry on the castle nut differentiates this from the slotted nut. Their functions and how they work are the same
-
Keps-K lock nuts
Designed for easy assembly. The attached free-spinning serrated washer creates tension against the material’s surface when installed onto a bolt. Note: overtightening will cause the nut to fail.
-
Prevailing torque nut
The distortion of the top threads creates locking action, which causes the nut to resist loosening due to shock and vibration. They are installed with the conical top up, which makes these one-way lock nuts.
-
Kwik Nuts
Plastic push-on nut is applied to a threaded bolt and tightened manually or with a spanner or other tool. It can only be loosened with a wrench. Used when quick assembly is a priority.
How to Choose the Right Nuts and Bolts?
Selecting the right nut and bolt depends on factors such as material, strength, size, and application. Here are some key considerations:
- Material: Nuts and bolts come in various materials, including stainless steel, brass, and carbon steel. Choose based on corrosion resistance and strength requirements.
- Thread Type: Coarse-threaded bolts provide better grip, while fine-threaded bolts are used for precision applications.
- Length and Diameter: Ensure the bolt length and diameter match the requirements of your project.
- Load Capacity: Consider the weight and stress the fasteners will bear to ensure durability.
Applications of Nuts and Bolts
Nuts and bolts are used in a variety of industries and applications, including:
- Construction: Bridges, buildings, and infrastructure projects.
- Automotive: Cars, motorcycles, and heavy machinery.
- Aerospace: Aircraft assembly and repairs.
- Furniture: Beds, tables, chairs, and DIY projects.
- Electrical Installations: Securing electrical panels and devices.
Maintenance and Safety Tips for Nuts and Bolts
To ensure longevity and safety, follow these maintenance tips:
- Regular Inspections: Check for loosened or corroded nuts and bolts.
- Proper Tightening: Use torque wrenches to apply the correct force.
- Lubrication: Prevent rust by applying anti-corrosion lubricants.
- Storage: Store nuts and bolts in dry conditions to avoid damage.
When to use bolts vs screws
Many people think the difference between bolts and screws is the tool used—screws need a screwdriver, while bolts need a wrench. But that’s not always true. Some bolts have heads like screws and need a screwdriver, while some screws use nuts. The distinction isn’t always clear.
There are so many different bolts and screws and some share similarities. Where they differ in general terms will help you decide which one to use:
Bolts | Screws |
|---|---|
Non-tapered | Tapered |
Uses a nut and washer | Uses a washer and sometimes a nut |
Threads provide stronger holding power | Threads provide sure grip |
Best for heavy-duty applications | Best for lighter applications |
Your choice depends on the application and the materials you’re fastening. For lightweight materials like plastic, plywood, and drywall, screws are usually the best option. Bolts are also available in plastic but are mainly used in electronics because they are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and provide good insulation.
Parts of a bolt
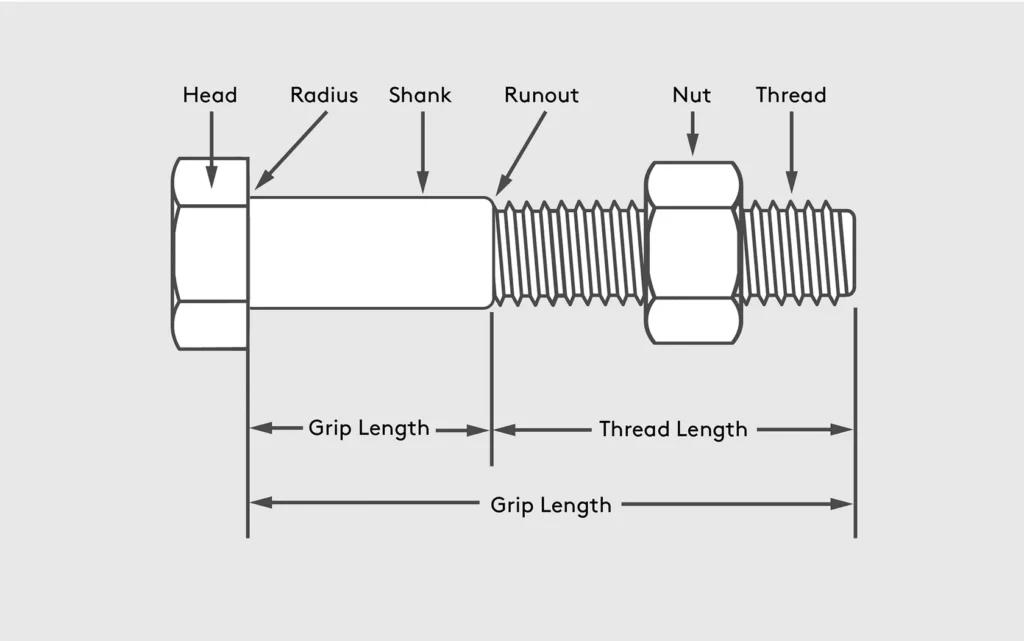
Understanding the anatomy of a bolt will help you choose what you need.
- Thread: The helical ridges that spiral around the body and engages with the nut.
- Runout: The point on the bolt that “runs out” of thread and where the shank begins.
- Shank: The smooth, threadless part of the bolt.
- Radius: The curve between the shank and the head.
- Head: The part of the bolt that a torque tool can hold for tightening or loosening.
- Thread length: The length of the thread, which varies according to its intended purpose.
Bolt sizes
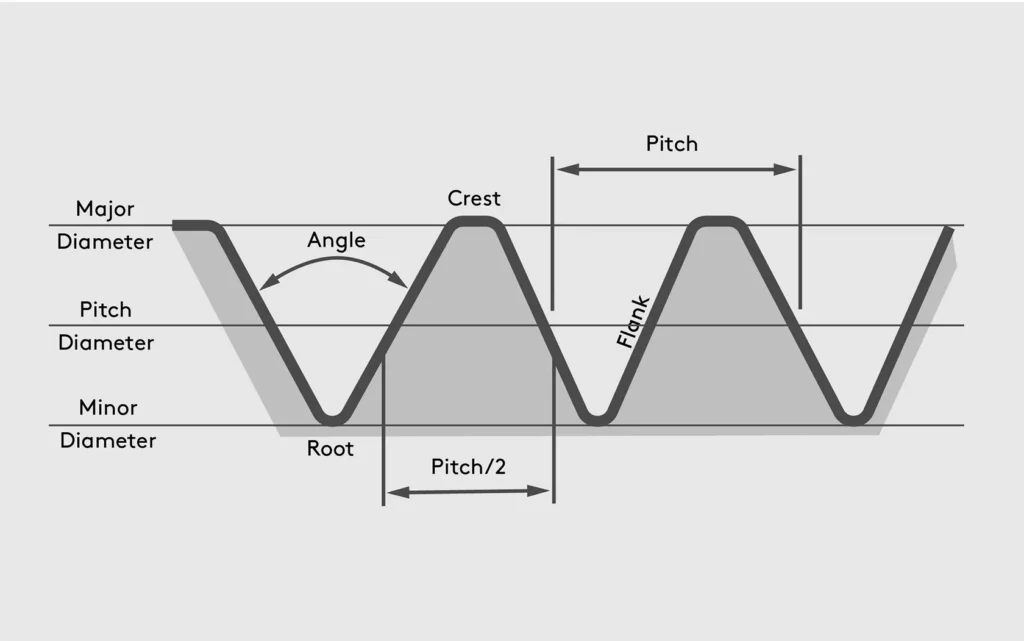
- Major diameter: Diameter of the imaginary cylinder from the top of an external thread.
- Minor diameter: Diameter of an imaginary cylinder from the thread’s groove.
- Crest: Prominent part of the thread.
- Root: Bottom of the groove between the two flanking surfaces of the thread.
- Flanks: Straight sides that connect the crest and the root.
- Thread angle: Angle between the flanks.
- Pitch: Distance, measured parallel to its axis, between corresponding points on adjacent surfaces.
Conclusion
Understanding the types of nuts and bolts and the difference between nut and bolt is essential for selecting the right fasteners for your projects. Whether you need screw nut bolt combinations for furniture or high-strength bolts for industrial applications, knowing the different types helps you make informed decisions. If you are looking for high-quality fasteners, check out Fasteners Manufacturers, Bolt Manufacturers in India, Tejdeep Steels, and Nuts Manufacturers in India for the best options.
By choosing the right nuts and bolts, you can ensure strong, durable, and secure assemblies in any application.

