Bolts play a crucial role in various industries, from construction and automotive to manufacturing and aerospace. Choosing the right bolt specification ensures durability, strength, and safety in applications. In this guide, we will explore bolt specification, bolt material, bolt sizes, and other essential details to help you make informed decisions.
What is a Bolt?
A bolt is a type of fastener with an external thread used to secure two or more components together. It requires a nut to hold it in place and provide structural integrity. Unlike screws, which thread into materials, bolts work in combination with nuts and washers.
Importance of Bolt Specification
Selecting the right bolt specification is essential for structural strength, durability, and safety. Incorrect specifications can lead to failure, resulting in accidents or material damage. Key factors in bolt specification include:
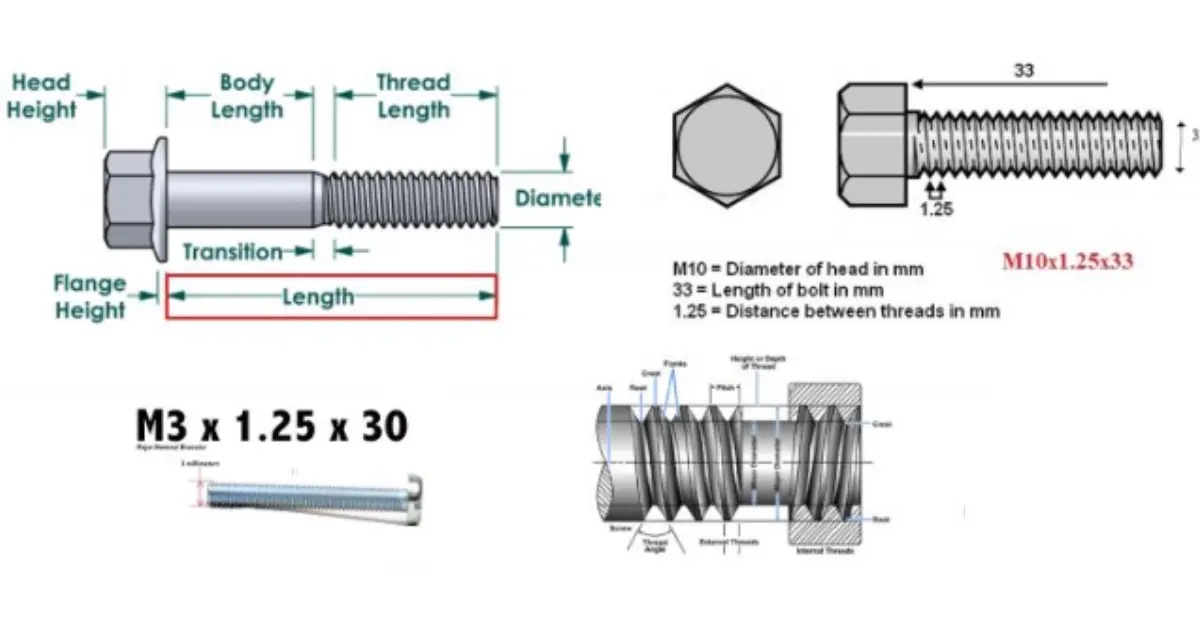
- Diameter and Length – Determines the fit and strength.
- Thread Pitch – Defines how tightly the bolt engages with the nut.
- Bolt Material – Influences corrosion resistance, durability, and mechanical strength.
- Tensile Strength – Indicates the bolt’s ability to withstand tension.
- Coating and Finish – Provides protection against rust and wear.
Types of Bolt Materials
The bolt material used affects strength, corrosion resistance, and usability. Some commonly used bolt materials include:
1. Carbon Steel Bolts
Carbon steel bolts are widely used due to their affordability and strength. They come in low, medium, and high-carbon variations.
- Low Carbon Steel – Used for general applications.
- Medium Carbon Steel – Offers higher strength and better resistance.
- High Carbon Steel – Suitable for heavy-duty applications.
2. Stainless Steel Bolts
Stainless steel bolts offer excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for marine and outdoor applications. Common grades include:
- 304 Stainless Steel – Good corrosion resistance.
- 316 Stainless Steel – Superior corrosion resistance, especially in saltwater environments.
3. Alloy Steel Bolts
Alloy steel bolts provide high strength and durability. They are used in high-pressure applications like automotive and aerospace industries.
4. Brass and Copper Bolts
These bolts are used for electrical and decorative applications due to their non-magnetic properties and corrosion resistance.
Standard Bolt Sizes and Dimensions
Understanding bolt sizes is crucial for selecting the right bolt for an application. Bolt sizes include:
- Diameter – Measured across the shank.
- Length – Measured from the base to the tip.
- Thread Pitch – Number of threads per inch (TPI) for imperial bolts or thread distance for metric bolts.
Common Bolt Sizes:
| Bolt Diameter | Thread Pitch | Common Lengths |
|---|---|---|
| 1/4 inch | 20 TPI | 1, 1.5, 2 inch |
| 5/16 inch | 18 TPI | 1.25, 2, 3 inch |
| 3/8 inch | 16 TPI | 1.5, 2.5, 4 inch |
| 1/2 inch | 13 TPI | 2, 3, 5 inch |
For metric bolts, sizes include M4, M6, M8, M10, M12, M16, and more.
Bolt Types:
| Anchor bolt |
Image credit: Portland Bolt |
Anchor bolts are embedded in concrete or masonry for structural applications. |
| Carriage bolt |
Image credit: Bolts ‘n Nuts Plus |
Carriage bolts are used to fasten metal to wood. The undercut of the bolt head is square to hold the bolt in place once tightened. |
| Elevator bolt |
Image credit: TOPS Inc |
A flat, plain or countersunk head with a squared undercut holds the bolt in place when a nut is tightened. These are common in conveyor systems. |
| Flange bolt |
Image credit: Packer Fastener & Supply |
Flange bolts have an integral washer on the undercut of the bolt head that distributes the bearing load. These are also known as frame bolts. |
| Hanger bolt |
Image credit: Monster Fastener |
A hanger bolt does not contain a bolt head. Both ends are threaded, but with one end containing a wood screw. |
| Hexagon bolt/Tap bolt |
Images credits: Portland Bolt; Fastwell Ind. Co. |
Hex bolts have six-sided heads. Tap bolts are threaded the entire length of the shank. |
| Lag bolt |
Image credit: MoWiNet |
Lag bolts are also called lag screws. They create their own mating thread in wood and other soft materials when tightened. |
| Machine bolt |
Image credit: Infly Industry Inc. |
Machine bolts are meant for assembling metal components through predrilled holes with an accompanying screw. These are more commonly called machine screws. |
| Plow bolt |
Image credit: K & R Supply, LLC |
With a countersunk flat head, a square shank neck, and a unified thread pitch, plow bolts are durable and common in construction devices. |
| Sex bolt |
Image credit: Wilson Glass |
Sex bolts do not require a nut. They come with a mating female component that covers the bolt shank. They are useful for fastening items that cannot be exposed to the abrasive threads. |
| Shoulder bolt |
Image credit: Unified Supply |
More commonly know as shoulder screws. Visit Tejdeep Steels Shoulder Screw Selection Guide and Specification Filter for tutorial information. |
| Square head bolt |
Image credit: Melfast |
Square head bolts a four-sided bolt head with a machine screw thread. |
| Stud bolt |
Image credit: Xiamen Landee Ind. Co. |
Stud bolts utilize hex nuts on both ends of the bolt. The workpieces are held between the two bolts. |
| Timber bolt |
Image credit: Jiaxing |
Timber bolts are explicitly meant for use with large wood planks and structures. They are common in lumber and marine industries. |
| T-head bolt |
Image credit: Shanghai Mountain Co. |
A T-head bolt has a T-shaped head which can fit into a slot or can be gripped easily by a wrench. |
| Toggle bolt |
Image credit: Johson Industrial |
With an expanding wing-like nut, toggle bolts are used to mount objects to walls. The nut inserts through a hole before it expands to lay flat against the surface. |
| U-bolt |
Image credit: Portland Bolt |
U-bolts are partially threaded on both ends and are bent in the shape of the letter ‘U’, with either a radius or two right angles. |
Nut Bolt Specification and Their Uses
Selecting the correct nut bolt specification is essential for efficiency and safety. The specifications are determined by factors such as:
- Material and Coating
- Strength Grade (e.g., Grade 2, Grade 5, Grade 8 for steel bolts)
- Thread Type (Fine, Coarse, or Metric)
- Head Style (Hex, Square, Flange)
- Application Suitability
Bolt Mechanical Properties
The bolt mechanical properties determine the bolt’s ability to handle loads, pressure, and environmental conditions. Key mechanical properties include:
- Tensile Strength – Measures resistance to breaking under tension.
- Yield Strength – The stress at which permanent deformation begins.
- Hardness – Resistance to surface deformation and wear.
- Ductility – The bolt’s ability to stretch before breaking.
Choosing the Right Bolt for Your Needs
When selecting a bolt, consider:
- Load Requirements – High-stress applications need high-strength bolts.
- Environmental Factors – Corrosive environments require stainless steel or coated bolts.
- Application-Specific Needs – Some bolts work best in specific uses, like anchor bolts for construction.
Where to Find High-Quality Bolts?
For high-quality fasteners, you can check fasteners manufacturers and Bolt manufacturers in India who provide reliable products for various industries.
Conclusion
Understanding bolt specification is essential for selecting the right bolt for any application. The bolt material, size, and mechanical properties play a crucial role in ensuring safety, durability, and efficiency. Whether you need nut bolt types, bolt dimensions, or custom fasteners, always refer to trusted manufacturers for the best products.
For the best bolts and fasteners, check out Tejdeep Steels, one of the leading providers of high-quality industrial bolts.
By choosing the correct bolts and nuts, you ensure the safety and longevity of your projects. Whether for construction, automotive, or industrial applications, always use the right bolts for a secure fit and optimal performance.